For any business focused on improving customer relationships and the related day-to-day operations, selecting the right open-source CRM is a strategic decision. It directly impacts how you manage customer data, monitor sales performance, and coordinate marketing activities.
Read this blog to learn about ways to determine the best pick for your Open Source CRM provider. But first, let’s understand the meaning of CRM to get your basics right.
What is a CRM, Really?
A CRM, or Customer Relationship Management system, is a digital infrastructure that helps businesses manage all interactions and data related to their prospects, leads, and existing customers. It consolidates customer details such as communication history, purchase behavior, support tickets, and ongoing sales activity into a structured, searchable format.
Rather than storing customer data across spreadsheets, emails, or different software tools, a CRM creates one organized interface for teams to access, update, and act on customer-related tasks. Businesses use CRMs to automate follow-ups, assign leads, manage pipelines, and generate reports based on activity and revenue trends.
Now, let’s explore what an open source CRM is.
Defining Open Source CRM
Open Source is a type of CRM where the source code is available freely for anyone to access, download, use and modify as per their needs. This allows internal tech teams or implementation partners to customize the CRM to align with the company’s business logic, workflows, and security frameworks. For growing companies, this level of control is often essential to ensure that the CRM adapts to their needs, not the other way around.
An open source CRM also allows teams to build new modules, adjust the database structure, and create workflows that reflect their internal processes. This level of control is especially beneficial for businesses that require more than just plug-and-play functionality. It removes recurring licensing costs, which often become a burden for small teams or early-stage ventures.
How to choose the right open-source CRM
Open source CRMs give you the opportunity to define exactly how the system should function, but they also place the responsibility of setup, integration, and maintenance on your team. This makes the selection process a critical step toward successful adoption.
Before choosing any solution, make sure you approach the evaluation as a set of small, objective decisions. The sections below explain how to move through that process.
1. Define Your Business Needs and Goals:
Start with clarity about what you expect the CRM to accomplish. Break this down into operational needs, such as:
- Tracking inquiries and follow-ups
- Managing sales pipelines
- Assigning tasks across departments
- Monitoring customer support performance
- Generating reports for internal review
In parallel, note the inefficiencies in your current tools or processes. If your sales team is losing track of leads or if support tickets lack follow-up, these become direct indicators for the kind of features you must prioritize.
Avoid getting distracted by broad feature comparisons early on. Instead, prioritize your internal processes and create a list of measurable improvements you expect the CRM to enable.
2. Explore Open Source CRM Options:
As you explore platforms, assess how well each one supports modular architecture, plugin systems, multilingual functionality, and industry-specific use cases. Some open source CRMs are better suited for service-based industries, while others offer more support for sales and field operations.
Take time to review user documentation, community support forums, and sample demo environments. These will help you understand how active the platform’s ecosystem is, which plays a direct role in future upgrades and security maintenance.
3. Evaluate Features and Functionality:
Once you have shortlisted a few open source CRM systems, evaluate how each one handles the following critical features:
- Workflow Automation: Can you set rules for lead routing, task escalation, and status updates?
- Integration Support: Does the CRM offer APIs or prebuilt connectors for email, calendars, accounting tools, or marketing systems?
- User Roles and Access Controls: Can you define who sees what, based on department or function?
- Reporting and Analytics: Are you able to configure custom dashboards and generate reports that support decision-making?
- Mobility and Cloud Hosting: Does the platform offer mobile access or cloud deployment flexibility?
4. Test and Implement:
After narrowing your list to one or two platforms, run a test instance in a controlled environment. Invite stakeholders from different teams to explore the interface, simulate tasks, and give feedback on usability.
Avoid relying only on product screenshots or comparison sheets. Actual hands-on usage is essential to validate assumptions. A platform that looks feature-rich may feel clunky in real scenarios, while a simpler interface may result in higher efficiency and faster adoption.
During the testing phase, observe how easy it is to:
- Import existing customer data
- Configure automation rules
- Set up user roles and permissions
- Connect external tools
- Access reports and insights without technical support
Once satisfied, plan your actual implementation in phases. Begin with a small set of users, expand gradually, and assign clear ownership for monitoring system performance, user onboarding, and data integrity.
Open Source vs. Proprietary (SaaS) CRM: A Head-to-Head Comparison
When selecting a CRM, businesses have to make the choice between adopting an open source CRM or a proprietary CRM (commonly offered as software-as-a-service or licensed products). Both approaches come with benefits, but their long-term implications differ significantly across cost, control, scalability, and dependency.
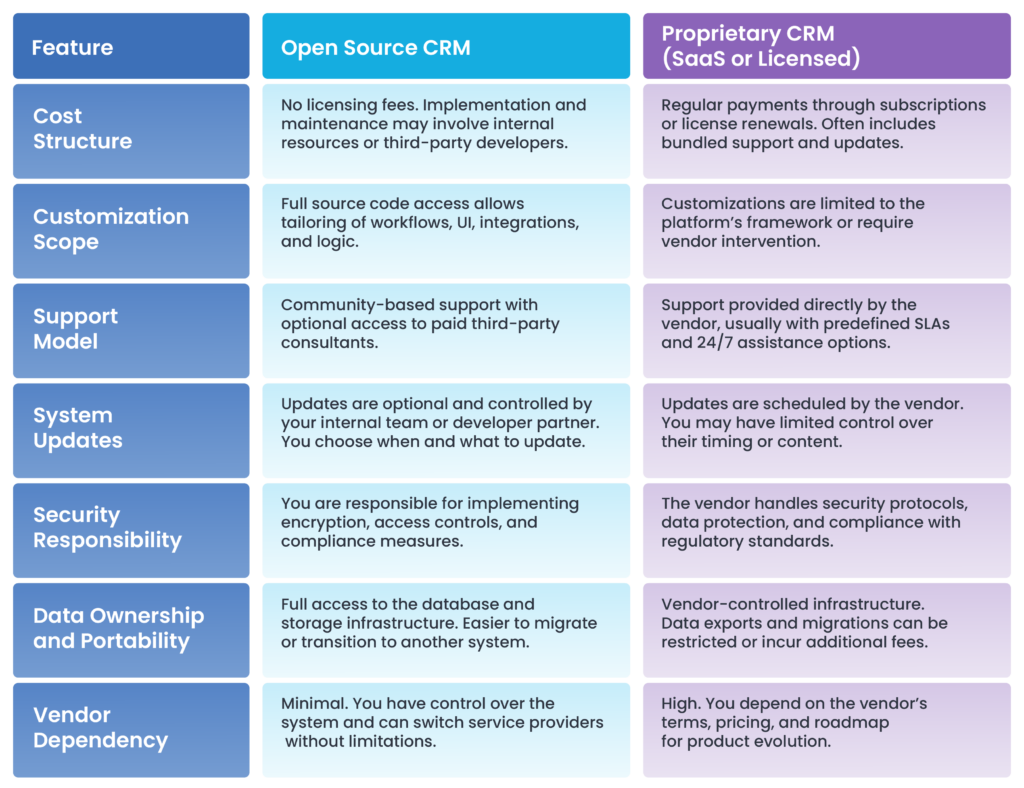
What are the advantages of open-source CRM software?
Organizations that adopt open source CRM platforms often do so for their ability to align closely with internal operations, cost priorities, and IT strategies. These systems remove rigid usage conditions and instead provide a structure that can evolve with your customer engagement goals.
Budget-Friendly Setup and Ownership
An open source CRM solution eliminates the need for annual licensing payments or packaged subscription tiers. This makes it suitable for businesses that want to reduce software acquisition expenses without sacrificing essential CRM capabilities.
Full Access for Tailored Adjustments
Open source CRM software is built to accommodate changes at the code level. Whether a company needs to integrate custom modules, adapt the data architecture, or fine-tune dashboard interactions, all these adjustments can be performed internally or with third-party development partners. This degree of control allows organizations to configure their CRM around their sales processes and service cycles rather than adjusting operations to fit the software.
Platform Independence and Control Over Usage
When you operate on open source software, you are not tied to vendor-defined pricing models, software restrictions, or data policies. You decide how the system is used, how often it is upgraded, and which components remain in place. This creates more freedom for scaling, migrating infrastructure, or switching IT providers without needing contractual permissions.
Data Location and Security Strategy of Your Choice
Open source CRM software gives you the flexibility to host customer data on any infrastructure that suits your business. Whether it is a private cloud server maintained by your IT team or a third-party hosting partner, you decide the security protocols, access controls, and backup policies. This level of autonomy is useful for businesses with compliance requirements or strict information governance rules.
Room to Expand Using AI and Automation
Many open-source CRMs can be enhanced with machine learning tools, automation libraries, and advanced analytics frameworks. Businesses are increasingly adding features like sales predictions, automated task triggers, or sentiment analysis to personalize client interactions.
Things to consider before choosing open-source CRM
Before finalizing an open source CRM system, businesses need to assess a set of practical factors. These considerations will directly impact implementation timelines, resource allocation, and system performance in the long run.
Technical Readiness
Open source systems need in-house or outsourced developers to handle setup, customization, and maintenance. Without technical support, deployment delays and errors are common.
Support Access
There is no dedicated helpdesk unless you opt for a paid support plan. Most assistance comes from online communities and documentation, which may not be fast or consistent.
Data Security and Compliance
Your team is responsible for data protection, encryption, and audit trails. If your operations fall under compliance laws like GDPR or RBI guidelines, manual enforcement is required.
System Scalability
Growth requires manual scaling of server resources, database optimization, and feature additions. Plan for future demands from the start.
Updates and Patch Control
Software improvements and bug fixes are not automated. Regular monitoring and manual upgrades are necessary to keep the CRM stable and secure.
Integration Compatibility
APIs and plugins may be available, but connecting your CRM to third-party tools requires testing, configuration, and version control.
Conclusion
Selecting the right open source CRM allows your business to operate on its own terms. It offers flexibility to configure workflows, modify features, and eliminate unnecessary license expenses.
Unlike fixed platforms, open source systems can be adjusted as your team’s structure, customer volume, or service approach changes. This approach supports both short-term improvements and long-term adaptability.
However, it also requires structured planning, technical oversight, and regular system maintenance. When implemented correctly, an open source CRM provides a dependable foundation to manage leads, service operations, and performance metrics without external restrictions or vendor dependencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
An open-source CRM is a customer management system that provides access to its original source code. Businesses can use it without licensing costs and also modify the code as needed. These platforms are supported by developer communities who contribute improvements, resolve issues, and create updates, making the system evolve over time based on user and business feedback.
Open-source CRMs provide access to code and complete freedom to customize. Proprietary CRMs limit code access and depend on the vendor for updates or feature changes. With open-source, users can shape the system as required, while proprietary options offer fixed templates, subscription costs, and vendor-defined timelines for enhancements or support.
Open-source CRMs offer major cost savings as they are free to use and adjust. Businesses can modify the platform to meet specific needs. Active communities accelerate problem-solving, helping improve the system continuously. With no vendor restrictions, you can introduce changes, build features, and adapt workflows without waiting for third-party approvals.
Yes, open-source CRMs need technical involvement. Setup, configuration, and upgrades require skilled professionals or external support. Unlike paid platforms, open-source CRMs often rely on user communities for guidance. Security patches and system updates must be handled manually. This model suits teams willing to manage operations and troubleshoot without vendor dependency.
Open-source licenses determine how you can legally use or modify the CRM. Copyleft licenses require you to keep any changes public under the same license. Permissive ones give you more flexibility, needing only license attribution. Understanding these rules helps ensure legal compliance, especially if you plan to share or distribute the modified version.
Not at all. Small businesses can save upfront costs and still use powerful CRM tools. For larger organizations, open-source CRMs provide scalability and custom development options. Whether it’s startup-level data structuring or enterprise-grade customization, the flexibility of open-source suits various business models and budgets.
A self-hosted CRM is managed on your own servers, giving full control over data, updates, and configurations. It needs in-house infrastructure and technical capability. Cloud-hosted CRMs, on the other hand, are hosted by a service provider. They reduce the management workload but may include hosting costs and give less control over the technical environment.
Support usually comes from user communities, documentation, or open forums. These platforms contain setup guides and discussions for resolving issues. Some open-source developers or third-party vendors also offer paid support packages for more structured assistance. Unlike proprietary models, customer care is not always bundled with the product unless you subscribe to a support plan.
Open-source CRMs can be highly secure if properly maintained. Since many developers review the code, issues can be spotted and fixed quickly. However, applying security patches and configuring the system safely is your responsibility. Without routine maintenance, the system could become exposed to threats, making consistent management crucial.
Yes, new features can be added easily. With full access to the CRM’s source code, development teams can create custom functionalities that suit unique business goals. Whether it’s building a new reporting module or integrating with other platforms, the CRM evolves as your business grows, without limitations set by commercial vendors.