In recent years, the entire global market has been observed to become packed and fierce. Consumers now have more options to choose from and increased access to information at any time, as compared to the past. In this setting, there is a single element within modern purchase habits that determines if a business expands or remains idle. That element is Customer Experience.
Customer Experience (CX) refers to the emotions customers have regarding each interaction with your business. It starts the instant someone learns of your brand and the experience they receive while engaging with your organization. For companies of any size, customer experience distinguishes a singular purchase from a lasting partnership. Therefore, getting it right leads to customers returning more frequently. It encourages others to endorse your brand and rely on you for more significant purchases.
Read this blog to know how businesses can implement it to strengthen their brand image.
What Is Customer Experience?
Customer Experience is the full journey a customer has with your brand. It includes discovery research, purchase, onboarding use, and any support or follow-up afterwards. Customer Experience covers product quality, delivery speed, and the tone of your communication. It also covers emotional elements such as trust, confidence, and feeling respected.
A good customer experience stays uninterrupted even when many people and systems are working behind the scenes.
- For a retail customer, customer experience might include how easy it is to find a product in store, how clear the product information is on your website, how fast the checkout is, and how supportive the staff are if something goes wrong.
- For a service subscriber, customer experience includes how clear the product demo is, how smooth the procurement and invoicing processes feel, and how reliable the onboarding and technical support are.
In all cases, customer experience combines practical tasks and emotional impressions to shape the customer perception.
Why Customer Experience Matters More Than Ever?
Customer Experience is a direct driver of growth in several ways. With the emergence of quick commerce, this notion of ‘comfort’ has been embedded into online purchases. Anything that is even slightly inconvenient may get sidelined! However, other than sustenance, there are other set of benefits that come along when your customer experience efforts have actually paid off:
- Customers who enjoy their interactions tend to buy more. When people trust a brand, they try new products and choose premium options. That raises average order values.
- Retaining customers is much cheaper than acquiring new ones. If you can improve customer experience to keep customers longer, you reduce your marketing cost per sale.
- Positive Customer Experience fuels word of mouth. Recommendations from friends, family, and colleagues often lead to faster sales than expensive advertising.
- As technology raises expectations, the absence of a good Customer Experience becomes a bigger liability. Customers expect quick answers and smooth digital journeys. If you fail to meet those expectations, they switch brands quickly.
- A consistent focus on customer experience reduces operational cost because fewer errors and complaints mean less time spent on fixes.
Key Elements of a Strong Customer Experience Strategy
A practical customer experience strategy brings a number of elements together. The following list of factors are the important ones you must include in your daily operations in order to make the most of every customer’s purchase journey.
Omnichannel consistency
Customers interact with brands across many touchpoints. They may see an ad online, search for details on a mobile phone, visit a store, make a purchase on an app, and message customer support on a messaging platform. Each touchpoint must feel consistent. When messages disagree or information varies across channels, customers get confused and frustrated. A good customer experience strategy ensures information and tone are aligned across the web store, social, and support channels.
Personalisation
Relevance increases value. Personalisation can be simple and highly effective. Remembering a repeat order preference, offering product suggestions based on past purchases, or sending relevant offers around a customer’s birthday makes the interaction feel personal. Personalisation helps customers feel recognised and increases repeat purchase rates.
Speed and convenience
Customers value speed and ease. Basic expectations include fast page loads, a seamless checkout process, and prompt responses to customer inquiries. And now that mobile usage is dominant, it is quite an obvious decision for businesses to optimise their channels for mobile-first experiences and reduce drop-offs significantly. A smoother customer experience converts more visitors to paying customers.
Emotion and empathy
How staff speak to customers matters more than ever. A calm listening tone and honest, clear explanations turn many negative situations into positive impressions. Training people to show empathy and to solve problems efficiently is a simple way to improve Customer Experience with limited cost.
Feedback collection and action
Collecting feedback is useful only when you act on it. Surveys after key interactions, quick feedback options in messaging and periodic customer interviews help you find what to fix. Closing the loop by telling customers you fixed an issue makes them feel heard and improves customer experience across the customer base.
Data-driven decisions
Customer Experience becomes repeatable when you measure it. Use metrics to identify weak points and test changes to see what improves outcomes. A CRM can centralize interactions and reveal patterns that lead to better decisions.
The CX Journey Key Customer Touchpoints Explained
Understanding the customer journey lets you design experiences that reduce friction and increase delight. The following list of common stages and touchpoints will allow you to understand the concept of customer experience at a deeper level.
Awareness
This includes advertising, social posts, search listings, and recommendations from friends. The first impression matters. Simple, clear messaging helps set expectations for the rest of the journey and reduces confusion, which improves customer experience from the outset.
Consideration
At this stage, customers compare options, read reviews, and look for details. Website content, product description, demos, and clear pricing are critical. Helpful information reduces hesitation and improves the likelihood of purchase, which boosts customer experience scores.
Purchase
The checkout experience is often the most fragile part of the journey. Payment flows, delivery options, and clear confirmation messages all shape how customers feel after they buy. Simple, secure, and transparent checkout steps reduce cancellations and improve customer experience.
Onboarding
After purchase, a good onboarding gives customers confidence in the product and reduces early churn. Welcome messages, setup guides, quick videos, and a proactive check-in during early use make the customer experience smoother.
Support and service
When issues arise, how quickly and competently they are resolved defines much of the ongoing relationship. Support channels that are easy to reach, clear in guidance, and fast in response increase trust and elevate overall customer experience.
Advocacy
Satisfied customers leave reviews, recommend your brand, and participate in referral programs. Encouraging advocacy by asking for feedback and rewarding referrals strengthens the Customer Experience for both future and current customers.
Common Challenges Businesses Face in Delivering a Great Customer Experience
Many organisations find it hard to deliver a great customer experience even when they want to. Here are the common problems and practical tips to overcome them.
Fragmented systems
When customer information lives in multiple places, staff cannot see the full story. That creates repeated questions and inconsistent responses. The fix is to centralise key customer data in a system that the team can access easily. A unified view makes responding faster and improves customer experience.
Lack of personalisation
Generic messages make customers feel anonymous. Start with simple personalisation rules such as using names and referencing previous purchases. Over time, build more data-driven personalisation to improve relevance and customer experience.
Inconsistent service across channels
Customers expect consistent answers whether they speak to support on a phone app or in store. Document common scenarios, provide scripts as guidance, and run training so the team gives aligned responses that preserve customer experience.
Slow response times
Delays harm conversions and cause complaints. Measure first response time, set targets, and automate routine replies for common queries. Automation should not replace human empathy, but should remove delays that harm customer experience.
Untrained staff
Employees face real pressure when they are not trained. Invest in training and role plays to help staff handle typical scenarios with confidence. Provide reference materials and quick escalation paths so staff can resolve issues that matter to customer experience.
No feedback loop
Collecting feedback without action wastes effort. Assign owners to follow up on feedback themes and measure whether fixes reduce complaints. Rapid visible action is a powerful way to improve customer experience credibility.
How to Improve Customer Experience: Actionable Tips
Every positive customer experience is the result of many small, thoughtful actions. From quick adjustments to deeper changes, these tips give businesses clear ways to improve how customers feel at every touchpoint.
Audit the current experience
Map the journey across customer segments and channels. Identify the top three points of friction that cause complaints or abandonment. A short, focused audit gives you the highest impact areas to address.
Train and coach staff
Focus coaching on empathy, communication, and clear resolution. Role plays and recorded calls provide examples to learn from. When staff see the impact of small changes, they are more motivated to improve customer experience.
Use a CRM to centralise interactions
CRM software stores conversation history, purchases, and preferences in one place. When staff have context, they can resolve issues faster and avoid making customers repeat information again which lifts customer experience.
Build a feedback loop and close it
Ask short surveys after key interactions and log feedback with a clear owner. When teams fix root causes share that progress internally and externally. Customers who see follow-up feel valued, which improves customer experience.
Optimise the mobile experience
Test common flows on low-end devices and slow networks; these scenarios are quite common in the under developed countries. Reduce form fields, use clear buttons, and keep navigation simple to reduce churn and lift customer experience on mobile.
Offer self-service options
A searchable knowledge base, helpful FAQs, and clear tutorial videos reduce support volume and speed up resolution for customers. Self-service is a quick path to better customer experience for routine tasks.
Leverage automation wisely
Chat automation and AI for first-line queries speed responses and capture intent. Make sure escalation to humans is seamless, so complex emotional issues are handled with care. The right mix of automation and empathy improves customer experience while controlling cost.
Start small and measure
Test one change at a time and measure its effect on a clear metric. Small experiments reduce risk and allow you to scale what works to improve customer experience steadily.
Measuring Customer Experience: Key Metrics to Track
Customer experience feels subjective, but the right metrics turn it into something measurable and actionable. Tracking both perception and operational data gives businesses a clear view of where improvements are paying off.
Net Promoter Score
A simple measure of recommendation likelihood that helps track loyalty over time. Combine NPS with an open question to learn what drives scores.
Customer Satisfaction Score
Specific surveys after an interaction that rate satisfaction. CSAT helps identify problems with particular processes that affect customer experience.
Customer Effort Score
Measures how easy a task was for the customer. High effort indicates friction that must be removed to improve customer experience.
First Contact Resolution
Tracks how often issues are solved in the first touch. High FCR reduces repeat work and increases customer experience by resolving problems faster.
Retention and churn
These long-term metrics connect customer experience with business outcomes. Improved retention shows that customer experience changes led to stronger relationships.
Operational metrics
First response time, average handling time, and resolution time reveal where processes slow down. Improving these reduces customer frustration and lifts customer experience.
Use dashboards to combine these metrics and review trends regularly. Set clear ownership for each metric and tie improvements to simple experiments that move the needle on customer experience.
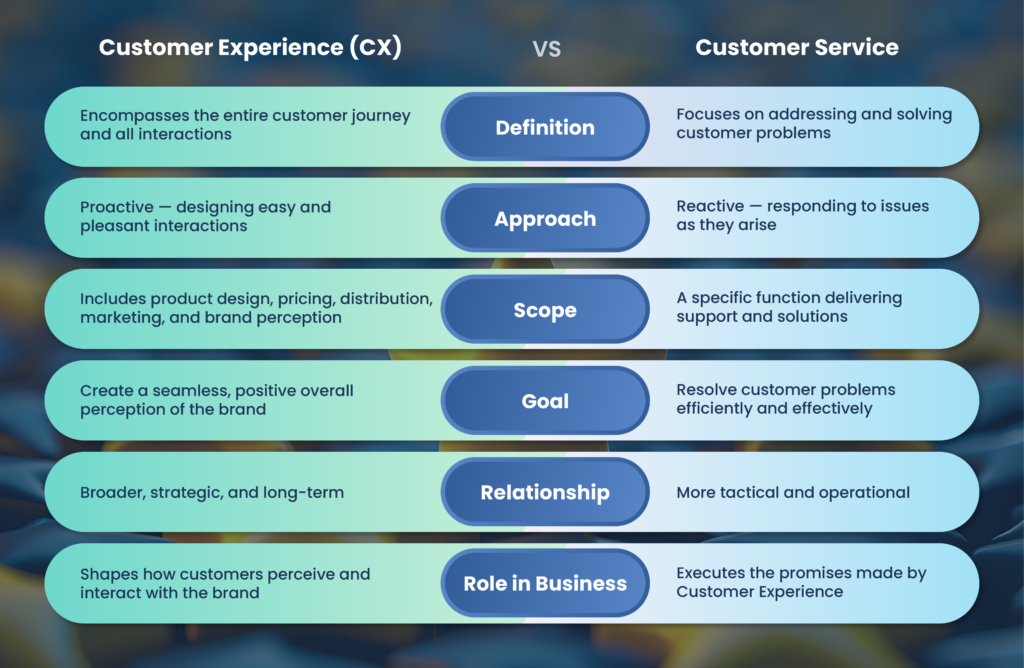
Customer Experience versus Customer Service: Key Differences
Customer Experience and customer service are connected but different. Customer service focuses on solving problems when they arise. Customer Experience covers the entire journey and looks at how to design interactions to be easy and pleasant by default. Customer Experience is proactive, whereas customer service is reactive. The tabular representation given below will help you understand the distinction in between them in a simplified manner:
How Small Businesses Can Compete with CX
Small businesses don’t need big budgets to create memorable customer experiences. And by using affordable, practical tools and focusing on what truly matters: clear communication, empathy, and genuine connections, they can stand out in any field.
The following strategies are easy to implement and can make a real difference in winning and keeping loyal customers.
Use WhatsApp Business
WhatsApp Business is a free and simple way to stay connected with customers. It lets you send quick replies, share order updates, and answer questions instantly. This direct line of communication helps your business feel accessible and responsive without any extra costs.
Ask for Reviews and Testimonials
Encourage happy customers to leave reviews or share testimonials. Positive feedback builds trust and attracts new customers. Display these reviews on your website and social media to show potential buyers that you care about their satisfaction.
Train Staff in Empathy
Empathy turns ordinary interactions into meaningful experiences. Train your team to listen carefully, understand customer concerns, and respond warmly. When customers feel heard and valued, they are more likely to return and recommend your business.
Keep Communication Quick and Clear
Respond promptly with clear, helpful information. Use tools like WhatsApp quick replies or email templates to save time while maintaining a personal touch. Quick, straightforward communication shows customers you respect their time and needs.
Use Free CRM Tools
Free customer relationship management tools help you organize contacts, track interactions, and schedule follow-ups. These platforms make it easier to personalize communication and build stronger, long-term relationships with your customers
Building a Customer-Centric Culture in Your Organisation
Building a customer-centric culture requires a clear and deliberate approach. Here are key steps to help your organization become truly focused on delivering exceptional customer experiences:
Leadership Buy-In
Senior leaders need to actively support customer-centricity. This means setting clear expectations, demonstrating customer-focused behavior, and embedding CX into strategic decisions, company values, and regular meetings. When leadership shows visible commitment, it helps make customer experience a core part of the organization’s identity.
Employee Training
Regular training is essential to help employees understand customer needs and develop empathy. Onboarding programs and ongoing workshops should teach staff how their roles impact customers and how to communicate effectively. Empowering employees with knowledge and the autonomy to make customer-first decisions boosts their confidence and effectiveness.
Regular Customer Feedback
Set up systems to collect feedback regularly through surveys, reviews, and direct outreach. It’s important that all departments receive this information and use it to improve products, services, and processes. Holding frequent discussions about customer insights keeps the entire organization aligned with customer needs.
Recognizing CX Wins
Celebrate employees who deliver outstanding customer experiences. Use shout-outs, awards, or incentives to recognize success stories. Public recognition encourages others to prioritize CX and strengthens the culture throughout the company.
Breaking Down Internal Silos
Encourage teams to collaborate across departments by focusing on customer journeys instead of isolated functions. Open communication and shared goals help everyone work together to resolve issues and provide seamless, end-to-end experiences.
| Further Reading Suggestions | ||
| What is a CRM | CRM Software | Mobile CRM |
| Open Source CRM | Sales CRM | What is AI CRM |
| Evolution of CRM | Analytical CRM | ERP Vs. CRM |
| Collaborative CRM | Mobile CRM | What is the CRM Process |
Conclusion
Customer Experience will be the crucial growth driver for every business in 2025. It influences reputation, revenue, and loyalty simultaneously. Begin with a thorough audit and prioritize significant adjustments that eliminate barriers and ensure customers feel appreciated. Utilize data to assess advancements, educate your staff in empathy, and equip teams with resources to provide uniform experiences.
Customer Experience is not an initiative that can be forgotten after one day of execution. It is an ongoing approach to managing the business that prioritizes customers in decision-making and creates lasting value through client servicing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Customer Experience means the total perception a customer forms about your brand based on every interaction from discovery to support. It includes both the practical elements, such as speed and accuracy, and the emotional elements, such as feeling respected and understood. Measuring customer experience with NPS, CSAT, and other metrics helps teams make targeted improvements that increase retention.
Customer service resolves problems and provides help at the moment. Customer Experience is broader and covers the entire journey, including product design, pricing, and communication. Customer service is a key part of Customer Experience, but the latter focuses on designing interactions to be simple, consistent, and pleasant to reduce the need for reactive service.
Customer Experience is an affordable growth tool for small businesses. Positive experiences lead to repeat business and referrals, which lower acquisition costs. Many customers rely on recommendations, so a strong Customer Experience builds trust in local markets. Small businesses can implement simple changes, such as better messaging or staff training, to get meaningful improvements in Customer Experience.
A good Customer Experience is when an order is easy to place, delivery is on time, communication is clear, and support resolves any issue quickly and fairly. A customer who feels confident and valued after an interaction is more likely to return and recommend the business, which reflects a strong Customer Experience.
Measure Customer Experience with perception metrics like NPS and CSAT, and operational metrics like first response time and first contact resolution. Segment the data by customer type and channel to find the most relevant problems to fix. Use a CRM to capture interactions and to connect metrics to outcomes like retention and repeat purchases.
Common mistakes include inconsistent messages across channels, slow responses, and ignoring feedback. Other problems are fragmented data and untrained staff. Fix these issues by centralising information, creating clear service standards, and running regular training to sustain improvements in Customer Experience.
Yes, technology such as CRMs, chat automation, and analytics can make interactions faster, more personalised, and more consistent. Technology helps scale good practices, but must be combined with clear processes and human oversight so Customer Experience remains warm and responsive to complex situations.
Personalisation makes interactions more relevant and reduces friction. When businesses remember preferences and tailor offers, customers feel understood. That feeling increases loyalty and boosts repeat business, which makes Customer Experience more valuable to the bottom line.
Start by mapping the customer journey and identifying major friction points. Talk to customers to learn what matters most. Train staff on communication and problem-solving, and implement a basic CRM to centralise interactions. Choose one metric to focus on and run small experiments to improve the Customer Experience.
All industries benefit, but sectors that rely on repeat purchases and long-term relationships, such as retail, hospitality, banking, and software, often see immediate returns. Service-oriented industries gain especially because customer interactions directly affect loyalty and referrals, which are essential for growth.



